Data Science And its Future
By Shreya Bansal

We hear a lot about how the artificial intelligence and machine learning are going to change the world and how the internet of things will make our life easier. But what’s the one thing which underpins all these revolutionary technologies, the answer is data from social media to IoT devices which generating immeasurable data. As the world entered the era of big data, the need for its storage also grew. It was the main challenge and concern for the enterprise industries until 2010. The main focus was on building framework and solutions to store data. Now when Hadoop and other frameworks have successfully solved the problem of storage, the focus has shifted to the processing of this data. Data Science is the secret sauce here. All the ideas which you see in Hollywood sci-fi movies can actually turn into reality by Data Science. Data Science is the future of Artificial Intelligence. Therefore, it is very important to understand what is Data Science and how can it add value to your business.
What is Data Science?

First, let’s see what is Data Science. Data Science is a blend of various tools, algorithms, and machine learning principles with the goal to discover hidden patterns from the raw data.
The answer lies in the difference between explaining and predicting.
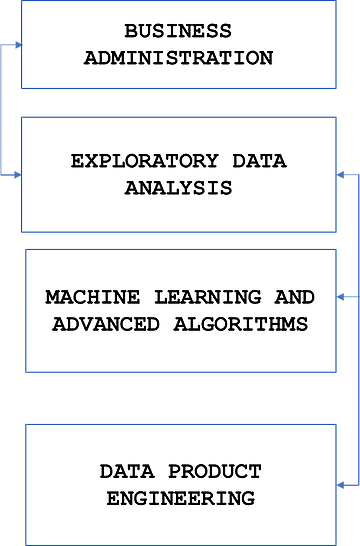
As you can see from the above image, a Data Analyst usually explains what is going on by processing history of the data. On the other hand, Data Scientist not only does the exploratory analysis to discover insights from it, but also uses various advanced machine learning algorithms to identify the occurrence of a particular event in the future. A Data Scientist will look at the data from many angles, sometimes angles not known earlier
8 Ways a Data Science Can Add Value to Business :–
1. Empowering management and officers to make better decisions
An experienced data scientist is likely to be as a trusted advisor and strategic partner to the organization’s upper management by ensuring that the staff maximizes their analytics’ capabilities. A data scientist communicates and demonstrates the value of the institution’s data to facilitate improved decision-making processes across the entire organization, through measuring, tracking, and recording performance metrics and other information.
2. Directing actions based on trends—which in turn help to define goals
A data scientist examines and explores the organization’s data, after which they recommend and prescribe certain actions that will help improve the institution’s performance, better engage customers, and ultimately increase profitability.
3. Challenging the staff to adopt best practices and focus on issues that matter.
One of the responsibilities of a data scientist is to ensure that the staff is familiar and well-versed with the organization’s analytics product. They prepare the staff for success with the demonstration of the effective use of the system to extract insights and drive action. Once the staff understands the product capabilities, their focus can shift to addressing key business challenges.
4. Identifying opportunities
During their interaction with the organization’s current analytics system, data scientists question the existing processes and assumptions for the purpose of developing additional methods and analytical algorithms. Their job requires them to continuously and constantly improve the value that is derived from the organization’s data.
5. Decision making with quantifiable, data-driven evidence.
With the arrival of data scientists, data gathering and analyzing from various channels has ruled out the need to take high stake risks. Data scientists create models using existing data that simulate a variety of potential actions—in this way, an organization can learn which path will bring the best business outcomes.
6. Testing these decisions
Half of the battle involves making certain decisions and implementing those changes. What about the other half? It is crucial to know how those decisions have affected the organization. This is where a data scientist comes in. It pays to have someone who can measure the key metrics that are related to important changes and quantify their success.
7. Identification and refining of target audiences
From Google Analytics to customer surveys, most companies will have at least one source of customer data that is being collected. But if it isn’t used well—for instance, to identify demographics—the data isn’t useful. The importance of data science is based on the ability to take existing data that is not necessarily useful on its own and combine it with other data points to generate insights an organization can use to learn more about its customers and audience. A data scientist can help with the identification of the key groups with precision, via thorough analysis of disparate sources of data. With this in-depth knowledge, organizations can tailor services and products to customer groups, and help profit margins flourish.
8. Recruiting the right talent for the organization
Reading through resumes all day is a daily chore in a recruiter’s life, but that is changing due to big data. With the amount of information available on talent—through social media, corporate databases, and job search websites—data science specialists can work their way through all these data points to find the candidates who best fit the organization’s needs. By mining the vast amount of data that is already available, in-house processing for resumes and applications—and even sophisticated data-driven aptitude tests and games—data science can help your recruitment team make speedier and more accurate selections.
Here are some of the leading data science careers you can break into with an advanced degree:
Business Intelligence (BI) Developer
WBI developers design and develop strategies to assist business users in quickly finding the information they need to make better business decisions.
Data Architect
Typical Job Requirements: Ensure data solutions are built for performance and design analytics applications for multiple platforms.
Applications Architect
Track the behavior of applications used within a business and how they interact with each other and with users.
Data Scientist
Find, clean, and organize data for companies. Data scientists will need to be able to analyze large amounts of complex raw and processed information to find patterns that will benefit an organization and help drive strategic business decisions.
Data Analyst
Transform and manipulate large data sets to suit the desired analysis for companies. For many companies, this role can also include tracking web analytics and analyzing A/B testing.